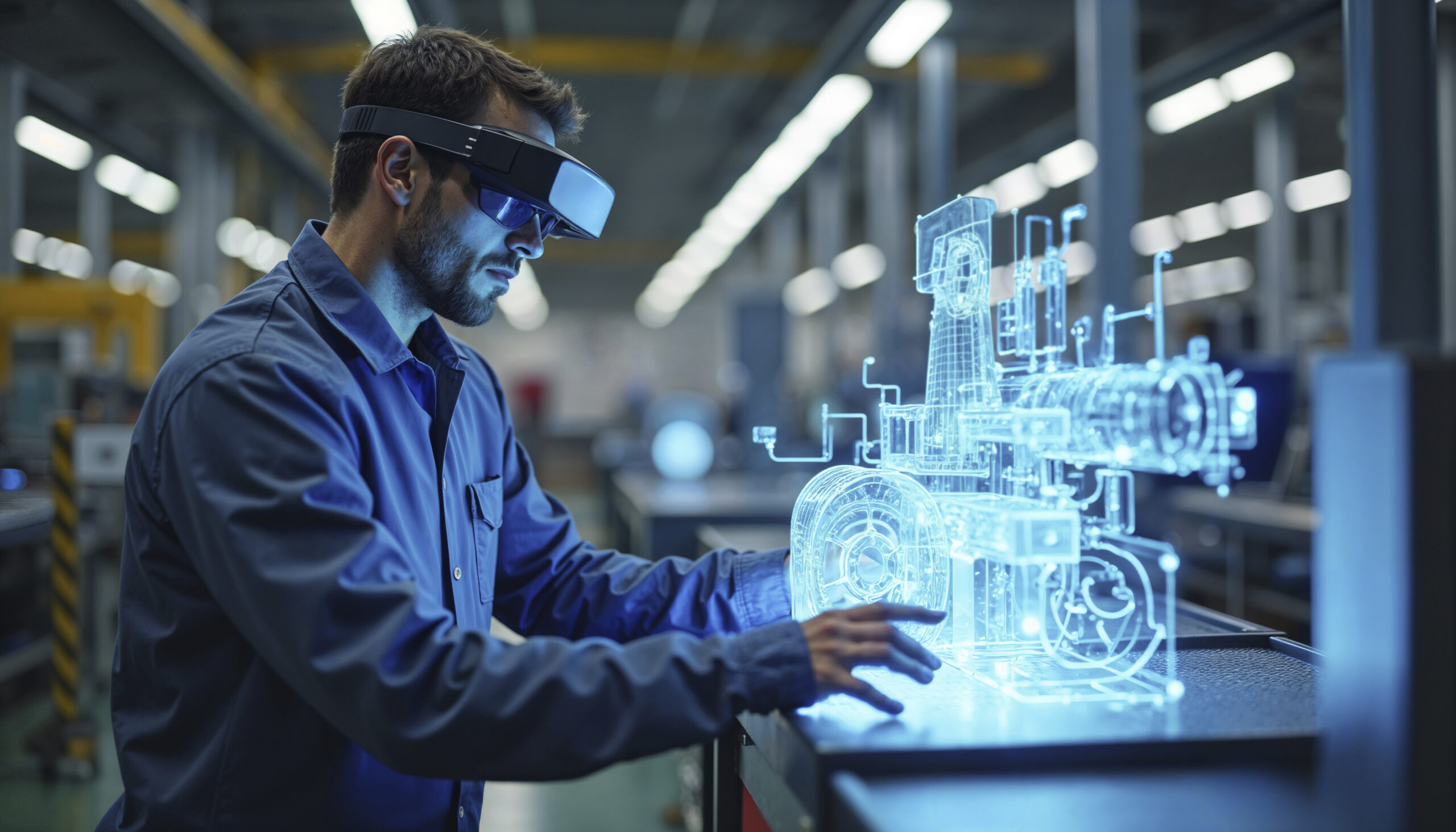
The global mining industry is entering a defining phase of digital reinvention, driven not by incremental efficiency gains but by a fundamental rethinking of how mining systems are designed and governed. For decades, mining has been shaped by heavy capital expenditure, volatile commodity cycles, harsh operating environments, and unavoidable safety risks. Today, however, the sector is absorbing technologies that were once exclusive to advanced manufacturing, aerospace engineering, and smart urban infrastructure. The convergence of digital twins, immersive metaverse environments, artificial intelligence, and autonomous systems is reshaping mining from the ground up, transforming it into a data-intensive, intelligence-led industry.
This convergence marks a decisive shift in how mining companies design assets, operate sites, train workers, and plan long-term strategies. Rather than reacting to incidents, breakdowns, or geological surprises after they occur, mining organizations are increasingly simulating outcomes before decisions are executed. Risk, once embedded in daily operations, is now being transferred into virtual environments where it can be analyzed, stress-tested, and mitigated without human or environmental exposure. This transition signals the beginning of a mining era where foresight replaces hindsight as the dominant operational philosophy.
Mining in the metaverse is not about gamification, virtual branding, or speculative digital experiences. Instead, it represents the construction of multi-layered, physics-accurate, continuously updated digital ecosystems that mirror real mining operations in real time. These environments integrate engineering models, geological data, live sensor feeds, and operational constraints into a single virtual framework that evolves alongside the physical mine.
Within these ecosystems, companies can safely test strategic decisions, train personnel, predict failures, and orchestrate autonomous actions without placing people, equipment, or ecosystems at risk. The metaverse thus becomes a parallel operational space one where experimentation is encouraged, failure is costless, and learning is accelerated. As a result, mining is evolving away from an experience-driven, trial-and-error industry toward a predictive, simulation-first model in which intelligence, not exposure, becomes the primary source of operational insight.
What Is a Digital Twin and Why Does It Matter in Mining?
A digital twin in mining is far more than a visual 3D representation of an asset or site. It functions as a living computational system that continuously reflects the physical mine’s state, behavior, and constraints. These twins incorporate models of equipment fleets, processing plants, ore bodies, ventilation systems, supply chains, and even human-machine interactions. Crucially, they are not static; they evolve in real time as new data flows in from IoT sensors, operational platforms, geological surveys, satellite imagery, and machine telemetry.
This real-time synchronization allows digital twins to represent not only what the mine looks like, but how it behaves under different conditions. Stress, wear, geological pressure, energy consumption, and operational bottlenecks can all be modeled dynamically. The digital twin becomes an executable model of reality capable of answering complex “what if” questions that traditional systems cannot address.
The strategic importance of digital twins in mining lies in their ability to transform uncertainty into foresight. Mining operations operate under extreme variability, where geological complexity, fluctuating commodity prices, unpredictable weather patterns, and mechanical degradation intersect continuously. Digital twins absorb this complexity and translate it into actionable intelligence. They reveal patterns, correlations, and emerging risks that remain invisible in conventional dashboards or reports.
By enabling virtual testing of interventions before physical implementation, digital twins reduce the cost of experimentation and dramatically lower operational risk. Decisions such as altering extraction sequences, modifying equipment usage, or adjusting logistics flows can be evaluated holistically allowing leaders to understand not only immediate outcomes but second- and third-order impacts across the entire operation.
More importantly, digital twins establish a shared, data-driven “single source of truth” across engineering, operations, safety, sustainability, and executive teams. Decisions that were once siloed such as changing blasting schedules, rerouting haulage paths, or modifying ventilation parameters can now be assessed collaboratively with full visibility into their implications for safety, productivity, energy use, emissions, and regulatory compliance. This alignment fundamentally improves governance and decision quality across mining enterprises.
Mining in the Metaverse: Immersive Virtual Worlds Meet Real Operations
When digital twins are embedded within immersive, interactive virtual environments, they form the operational backbone of the mining metaverse. This metaverse is not a separate or fictional universe, but a persistent digital extension of real mining operations one that exists alongside physical assets and continuously exchanges data with them. Planning, training, experimentation, and optimization can all occur within this shared virtual space.
In these environments, entire mining complexes can be explored at full scale and in full detail. Engineers and operators can walk through underground tunnels, inspect processing plants, and observe equipment behavior in three dimensions, while simultaneously accessing live performance metrics, safety indicators, and predictive alerts. This spatial intelligence dramatically enhances comprehension, enabling teams to understand complex systems intuitively rather than abstractly.
The immersive nature of the mining metaverse also improves collaboration and decision-making. Complex trade-offs such as balancing production targets against safety margins or energy constraints become easier to evaluate when stakeholders can see and experience outcomes rather than interpret spreadsheets. This is particularly valuable for large-scale, interconnected operations where small decisions can cascade into significant consequences.
Equally transformative is the metaverse’s ability to enable global collaboration. Specialists located anywhere in the world can enter the same virtual mining environment, analyze the same data, and contribute insights in real time. For remote, hazardous, or politically sensitive sites, this capability reduces the need for physical travel while expanding access to global expertise. In effect, the mining metaverse dissolves geographical barriers to operational intelligence.
Operators Train in Immersive VR/AR Worlds
Training has historically been one of the most hazardous and costly components of mining operations. New workers often acquire skills in live environments, where errors can result in injuries, equipment damage, or production losses. Immersive VR and AR training environments fundamentally disrupt this model by enabling experiential learning without physical exposure.
Within metaverse-based training systems, workers can repeatedly practice operating heavy machinery, navigating underground environments, and responding to high-risk scenarios such as cave-ins, equipment failures, ventilation breakdowns, or hazardous material releases. These simulations are built using the same layouts, equipment specifications, and operational conditions as the real mine, ensuring that training remains context-specific rather than abstract.
Beyond safety, immersive training accelerates skill acquisition and knowledge retention. Workers learn by doing rather than observing, developing muscle memory and situational awareness in a controlled setting. This approach is especially valuable as mining operations become more automated and technologically complex, requiring workers to interact with advanced systems rather than purely mechanical equipment.
Over time, these training environments become adaptive intelligence systems. By tracking trainee decisions, reaction times, and error patterns, AI-driven platforms can personalize learning pathways, identify systemic skill gaps, and continuously refine training content. The outcome is a workforce that is not only safer, but also more adaptable, technologically fluent, and prepared to operate in hybrid human–machine environments.
Risk Predicted Before It Happens
Traditional mining risk management has relied heavily on historical data, standardized safety protocols, and human judgment. While these methods have reduced incidents over time, they remain fundamentally reactive. Digital twin ecosystems enable a paradigm shift toward predictive and anticipatory risk management, where hazards are identified and mitigated before they manifest physically.
By simulating thousands or even millions of operational scenarios, digital twins can evaluate how changes in geology, equipment condition, weather, or operational sequencing interact to create risk. For instance, a digital twin can predict how prolonged equipment operation under specific loads increases failure probability, or how subtle geological stresses might compromise underground stability months in advance.
This predictive capability allows operators to intervene early by adjusting maintenance schedules, reinforcing structures, rerouting operations, or modifying production plans. Instead of responding to alarms after thresholds are crossed, teams can act proactively, often at significantly lower cost and risk.
Crucially, digital twin risk models improve continuously. By learning from both simulated outcomes and real-world events, these systems refine their predictions over time, becoming more accurate and context-aware. Risk management thus evolves from a static compliance function into a dynamic, intelligence-driven discipline embedded at the core of operations.
Autonomous Planning and Control
The long-term vision of mining in the metaverse extends well beyond simulation and training into autonomous planning and execution. Digital twins provide the cognitive foundation that makes autonomy viable by offering machines and algorithms a continuously updated, system-wide understanding of the operational environment.
In this paradigm, autonomous haul trucks, drills, and processing systems operate based not only on local sensor inputs but also on insights generated within the virtual twin. Planning algorithms simulate multiple production strategies, evaluate trade-offs across cost, speed, safety, and sustainability, and deploy optimized instructions back into the physical mine.
This creates a powerful feedback loop in which physical operations inform virtual simulations, and virtual intelligence guides physical execution. Over time, mining systems become increasingly self-optimizing, capable of adjusting to changing conditions without constant human intervention. Human oversight shifts from direct operational control to strategic governance, ethical oversight, and exception management.
Use Cases: How Companies Are Applying Digital Twin Metaverse Thinking
Across the global mining sector, leading companies are already applying digital twin and metaverse-inspired approaches to gain strategic advantage. Large-scale operations are modeling entire value chains from extraction and processing to logistics, storage, and export terminals within unified digital environments that provide end-to-end visibility.
These implementations are delivering measurable benefits. Predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime, virtual risk testing improves safety outcomes, and simulation-based planning enhances capital efficiency by validating expansion or modernization projects before physical investment. In parallel, digital twins support sustainability initiatives by modeling energy use, emissions, water consumption, and land impact under different operational scenarios.
As these systems mature, they are increasingly integrated with enterprise platforms, enabling executive teams to explore strategic scenarios such as commodity price volatility, regulatory changes, or supply chain disruptions—within the same virtual environments used for operational planning. This alignment bridges the gap between operational reality and strategic decision-making.
Training, Risk, and Autonomy: The Three Pillars of Mining Metaverse Impact
Zero-Risk Training
Zero-risk training represents one of the most immediate and transformative impacts of mining metaverse ecosystems. By removing physical danger from the learning process, organizations can accelerate workforce development, standardize skills across sites, and significantly reduce incidents linked to inexperience. Continuous access to realistic simulations also allows experienced workers to rehearse rare but high-impact scenarios, strengthening organizational resilience.
Predictive and Preventative Risk Modelling
Digital twin-driven risk modeling elevates safety from a compliance requirement to a strategic capability. Instead of reacting to incidents, organizations can anticipate them, quantify probabilities, and test mitigation strategies virtually. This proactive approach improves safety outcomes while also reducing insurance costs, regulatory exposure, and operational disruptions.
Autonomous Planning and Control
Autonomy represents the ultimate evolution of mining transformation. As digital twins gain fidelity and AI systems mature, autonomous planning will extend across entire mining ecosystems. Human leaders will focus on setting objectives, constraints, and ethical parameters, while intelligent systems execute within those boundaries—optimizing performance continuously.
Challenges and What’s Next
Despite its transformative potential, mining in the metaverse faces real challenges. Integrating heterogeneous data sources into coherent digital twins requires strong data governance, interoperability standards, and cybersecurity frameworks. Many mining sites also lack the connectivity and computational infrastructure required for real-time simulation and immersive collaboration.
Equally important is the human dimension. Organizations must invest in upskilling workers and leaders to interpret, trust, and act on virtual intelligence. Cultural resistance, change management, and governance models will play as significant a role as technology itself.
Yet, these challenges are rapidly becoming strategic priorities rather than barriers. As costs decline, infrastructure improves, and success stories multiply, digital twin ecosystems are transitioning from experimental pilots to foundational operational infrastructure.
Toward a Zero-Risk, Intelligence-Led Mining Future
Mining in the metaverse represents a fundamental redefinition of how the industry manages risk, complexity, and human capability. By combining digital twins, immersive environments, AI, and autonomy, mining companies are constructing systems where learning occurs virtually, risk is anticipated rather than endured, and decisions are guided by continuous, system-wide intelligence.
This evolution does not eliminate the human role in mining it elevates it. In a zero-risk, simulation-driven future, people move from exposure and reaction to oversight, strategy, and innovation. For an industry built on extracting value from the earth, the most valuable resource of the next era may be virtual insight powering real-world transformation.
Related Blogs: https://arabworldleaders.com/category/articles/